
By Robert Trefz
Load banks provide solutions for testing and maintaining power and cooling systems within data center facilities. Data centers are crucial in supporting modern economic operations, facilitating technologies utilized in industrial and manufacturing setups, transportation, logistics, banking, education, entertainment, and beyond. The recent surge in digitization, propelled by shifts in business interactions and remote work trends, has amplified the significance of data centers. Their capacity to provide essential services hinges on the uninterrupted availability of electrical power.
The financial repercussions of downtime vary based on the data center type and the scale of the outage. Beyond the monetary aspect, downtime hinders users from accomplishing critical tasks, influencing the reputations of service providers, and potentially leading to penalties for failing to meet service level agreements. Given the pivotal role of power availability in delivering dependable services, the verification of power and cooling system capabilities becomes paramount in maintaining service continuity. Load banks are a valuable tool for testing and validating the performance of data center power and cooling systems, ensuring optimal operation and minimizing downtime risks.
HOW ARE LOAD BANKS USED IN DATA CENTERS?
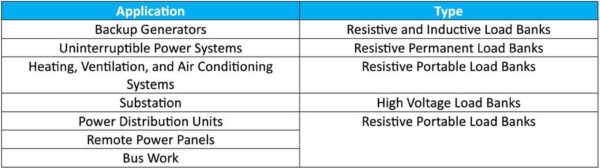
There are several applications for load banks in data centers such as commissioning, expansion, and maintenance. Load bank and test type will vary based on the application.
COMMISSIONING
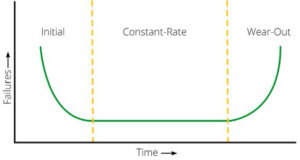
Throughout the life cycle of equipment, one can anticipate fluctuations in failure rates based on the equipment’s relative age. As illustrated in Figure 1, the early stages of the life cycle typically exhibit high initial failure rates. However, as defective products are identified and installation errors rectified, the failure rate decreases. Subsequently, the equipment tends to operate with relatively low rates of failure. Towards the end of their service life, products may experience a resurgence in failure rates.
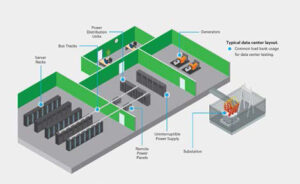
Commissioning is the meticulous process of verifying equipment thorough testing upon installation, ensuring it aligns with the end user’s requirements. This comprehensive procedure aids in uncovering potential issues and guarantees the proper and efficient functionality of components and systems. In the context of data center commissioning, critical systems undergo testing, encompassing backup diesel generators, uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), heating, ventilation, and cooling (HVAC) systems, electrical bus and distribution cabling, power distribution units, and remote power panels. This important step of load testing during commissioning allows for the identification and/or replacement of faulty components or systems before handing over the facility to the end-user. Given that the full facility load might not be consistently available during construction and commissioning, load banks serve the purpose of supplementing loads to simulate design conditions and to verify expected function.
MAINTAINING PROPER TEMPERATURE AND HUMIDITY
In some cases, data centers are commissioned and are operational before all the servers have been installed. In this situation, it may be difficult to maintain proper operating temperature and humidity ranges as the data center’s cooling system was designed with the expectation that servers are installed at capacity. Load banks can be used to replicate the heat load that would normally be created by the yet-to-be installed servers keeping the temperature and humidity within specification.
EXPANSION
Data centers are frequently designed with future expansion in mind. When expansion takes place, it becomes essential to test the operability and efficiency of new systems and components under load. Accurate simulation of the latest power and heat loads is crucial for this testing phase, and load banks play a key role in executing these tests. Employing multiple load banks helps simulate the electrical load that the new equipment will impose on the power distribution systems. Additionally, strategically placing resistive load banks at key points enables the verification of local cooling system performance. The resulting data can be automatically compiled into reports, providing evidence of compliance to customers who are purchasing server space.
MAINTENANCE
Many data centers employ a combination of backup UPS systems for short power interruptions and diesel generators for prolonged outages. Regular maintenance and testing of these systems are essential to guarantee their availability. Load banks are the most effective way in efficiently testing and subjecting electrical systems to stress for maintenance and periodic testing requirements. Various load test configurations can be tailored for specific maintenance purposes in these applications. The generated reports pinpoint identified issues, enabling prompt resolution.
EQUIPMENT UPGRADES OR REPLACEMENTS
Upon replacement or repair of specific components or equipment, it is critical to validate their correct functionality. Load testing serves as an effective method to ensure the proper function and performance of repaired or replaced equipment before it is reintegrated into service.
WHAT TYPES OF LOAD BANKS ARE USED IN DATA CENTERS?
Load bank elements use resistive, inductive, or capacitive loads on circuits, or a blend of these. In the testing of data center systems, it is important to choose load banks that offer the specific type of load aligning with the characteristics of the equipment being tested. For example, circuits predominantly serving motor loads should undergo testing using an inductive load bank.
BACKUP DIESEL GENERATORS
Most data centers rely on one or more onsite diesel generators to supply power during utility outages. Ensuring the correct operation and maintenance of these generators is essential for maximizing data center uptime.

Load bank testing is instrumental in verifying the availability and performance of generators. By simulating electrical loads, load banks help identify potential issues, enabling corrective actions to ensure backup power is readily available when needed. The load test serves to confirm the proper functioning of various components such as the voltage regulator, governor, cooling system, fuel system, and control system within an engine-generator.
Applying load during testing also mitigates the risk of diesel “wet stacking,” a phenomenon occurring when generators operate with insufficient load. This condition can lead to the accumulation of unburned fuel residues, impacting engine components and potentially compromising reliability.
The choice between a purely resistive or a resistiveinductive load bank depends on the testing requirements. A purely resistive load bank evaluates the engine’s ability to provide the rated kW and deliver an equivalent amount of kVA. On the other hand, a resistive-inductive load bank comprehensively tests the power supply by applying impedance currents out-of phase with voltage.
Periodic load testing of diesel generators is essential, adhering to regulatory standards, industry codes, and customer requirements. In larger data centers with substantial loads, permanently installed, containerized resistive-inductive load banks are often deployed to provide sufficient load capacity and withstand outdoor environmental conditions.
Leading load bank suppliers offer advanced control systems that facilitate automatic and transient load tests. The results of these tests can be archived and reviewed to assess generator performance over time. Alternatively, load bank control can be integrated into existing control systems commonly found in larger data centers.
HVAC SYSTEMS
Inadequate cooling can adversely affect the reliability of servers and other IT equipment. Load banks play a necessary role in HVAC commissioning processes. Given that load banks generate heat as they dissipate electrical power, they are employed to replicate the heat output of IT equipment. By observing an HVAC system’s response to this simulated heat, the effectiveness of the cooling system can be assessed. Throughout this process, load banks can be strategically relocated to specific areas to evaluate the local performance of the HVAC system. The networking of these load banks allows for centralized control, operated conveniently from a single hand-held device, optimizing operator efficiency, and ensuring consistent load application. Operators have the flexibility to adjust the operation of individual load banks to create targeted hot spots as necessary.
UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER SUPPLIES (UPS)
At its most basic level, a UPS comprises enclosed battery packs that automatically deliver power to loads in the event of a power failure. UPS systems prove particularly valuable in supplying power during the initial stages of an outage until the facility’s backup power generation system can provide acceptable power. Although a UPS may only need to operate for a brief duration, the seamless transition of power sources is vital for the uninterrupted functioning of downstream IT loads.
Load testing serves to validate the proper operation and performance of a UPS system. Utilizing one or more load banks, batteries are discharged in accordance with manufacturer specifications, assessing their capability to supply the required power. Additionally, the electrical performance of UPS inverters and distribution equipment undergoes evaluation to ensure accurate operation.
Typically integrated into scheduled maintenance programs alongside other backup power sources like diesel generators, UPS systems are commonly tested using resistive load banks.
ELECTRICAL SUBSTATIONS
Ensuring the reliability and sufficiency of power supplied to a data center from a substation is essential to meet the demands of IT power. Load banks are a standard tool in testing substations to confirm their capacity to deliver rated power and to validate the performance of relays and meters. Additionally, load banks can be employed alongside a transformer to assess the medium and high voltage feeds.
POWER DISTRIBUTION UNITS
Power Distribution Units (PDUs), when rack-mounted, play a pivotal role in controlling and monitoring power to servers, switches, and other devices. During the commissioning process, resistive load banks are frequently employed to test PDUs and validate their proper operation. Given that PDUs are often sized between 100 to 300kVA, mobile castor-mounted load banks are commonly utilized for testing purposes. Portable load banks can be strategically placed at each PDU within the data center hall, allowing for the application of power and continuous monitoring of PDU operation. Conducting load tests on PDUs proves to be a cost-effective method, ensuring that multiple racks receive the necessary power for downstream equipment.
REMOTE POWER PANELS
Remote Power Panels (RPPs) work in tandem with PDUs. Functioning as a distinct enclosure, an RPP facilitates a sub-feed from a PDU to connect to a distribution panel that, in turn, supplies power to load equipment. The use of an RPP offers the flexibility of siting PDUs in separate rooms and accommodates the use of larger PDUs equipped with sub-feed breakers. Load banks are routinely employed in commissioning RPPs to verify their proper operation and to ensure the effective distribution of power from the PDU to the rack systems.
BUS TRACKS
The adoption of bus track power distribution is increasing in data centers, providing enhanced flexibility and adaptability to accommodate growing power densities. Load banks are employed to assess the efficiency of bus track power units, feed tracks, and tap-offs, ensuring their optimal operation.
CONCLUSION
Data centers play a crucial role in delivering essential services that heavily depend on a consistent supply of electrical power. As the continuous availability of power is paramount for reliable services, verifying the capabilities of power and cooling systems becomes a key aspect in ensuring service continuity. Therefore, load banks are employed for the commissioning, expansion, maintenance, and testing of power and HVAC systems, including replacement equipment to ensure data center success.
Robert Trefz is Vice President of Marketing at Avtron Power Solutions. He can be reached at [email protected].