22
7X24 MAGAZINE FALL 2015
changes in each cycle depending on
the number in the license scope.
thus, the owner is entitled to install,
run, and request maintenance and
support for the software as long as an
active subscription is maintained. in
the perpetual license, however, the
owner pays an initial cost to purchase
the use of the software for the defined
number in the license scope. the
initial cost usually is inclusive of
maintenance services for the first year.
in addition, the owner may opt not to
have official maintenance services for
subsequent years without affecting his
rights to the use of the solution. table
2 summarizes the main differences
between these two license models.
Considering the case of a high
performance computing (hpC) data
center with a large number of nodes
(in thousands), a perpetual site license
will be more effective. it is expected
that all of the hpC nodes need the
monitoring template, with a few
exceptions to cater to some business
requirements. thus, the site license
will be more efficient since all
managed devices are almost identical.
D. AGENT VS. AGENTLESS
there are two approaches to apply
the monitoring to computing
infrastructure components: agent-
based and agentless monitoring. each
approach brings its own pros and
cons. a key decision on choosing a
monitoring solution is to decide
whether to look for agent-based or
agentless solutions. the agent-based
monitoring solution consists of a of
software component, typically a small
application, residing on the client
server and collecting data. the data is
then returned to the monitoring
station based on a policy within the
local agent, or as requested by the
monitoring server. in this practice, the
agent is very lightweight but able to
access granular metrics for better
monitoring, alerting and reporting, as
well as deeper levels of root-cause
analysis and trouble shooting. in
addition, advanced capabilities and
functions, such as patching and
configuration management, can be
encapsulated within the agent itself.
furthermore, agent-based solutions
allow for more flexibility with the
creation of customized service
monitors.
however, some agents are very heavy
consumers of resources and can stress
the servers they are monitoring; this
could eventually reduce the
performance of the servers they are
monitoring. this is an important
decision when considering hpC data
center monitoring, in which resource
utilization is crucial. in addition,
agents introduce considerable
support and administrative overhead
to ensure their compatibility with the
running system’s health, and that they
do not introduce any security
breaches to the environment.
Moreover, agent-based solutions
could limit the scalability of the
solution to the number of agents it
can manage, which is an important
metric for a large hpC environment.
the agentless solution, however, does
not require specific software
component to deploy the monitoring,
which solves most of the problems
introduced by the agent-based
solution. Generally, they rely on
standard system apis or network
packet analysis methods.
there are different methods used in
practice for agentless monitoring:
such as snMp (simple network
Management protocol) for
linux/uniX, network device and
storage filers; wMi (windows
Management instrumentation) for
windows-based systems; ssh (secure
shell) for linux/uniX systems [9]. for
snMp to work, however, the snMp
agent must be configured and
enabled to send/receive snMp traps.
but, it is still widely accepted that
snMp monitoring is considered
agentless since the agents are
standard software components within
the monitored systems. thus,
agentless does not require any
specific software to install on
managed devices, eliminating all
overhead associated with agent-
based systems.
on the other hand, agentless
solutions will be affected by
networking issues. also, when
monitored systems are highly utilized,
which is the norm in hpC
environments, agentless solutions
might lose the ability to connect to
those servers and collect required
data.
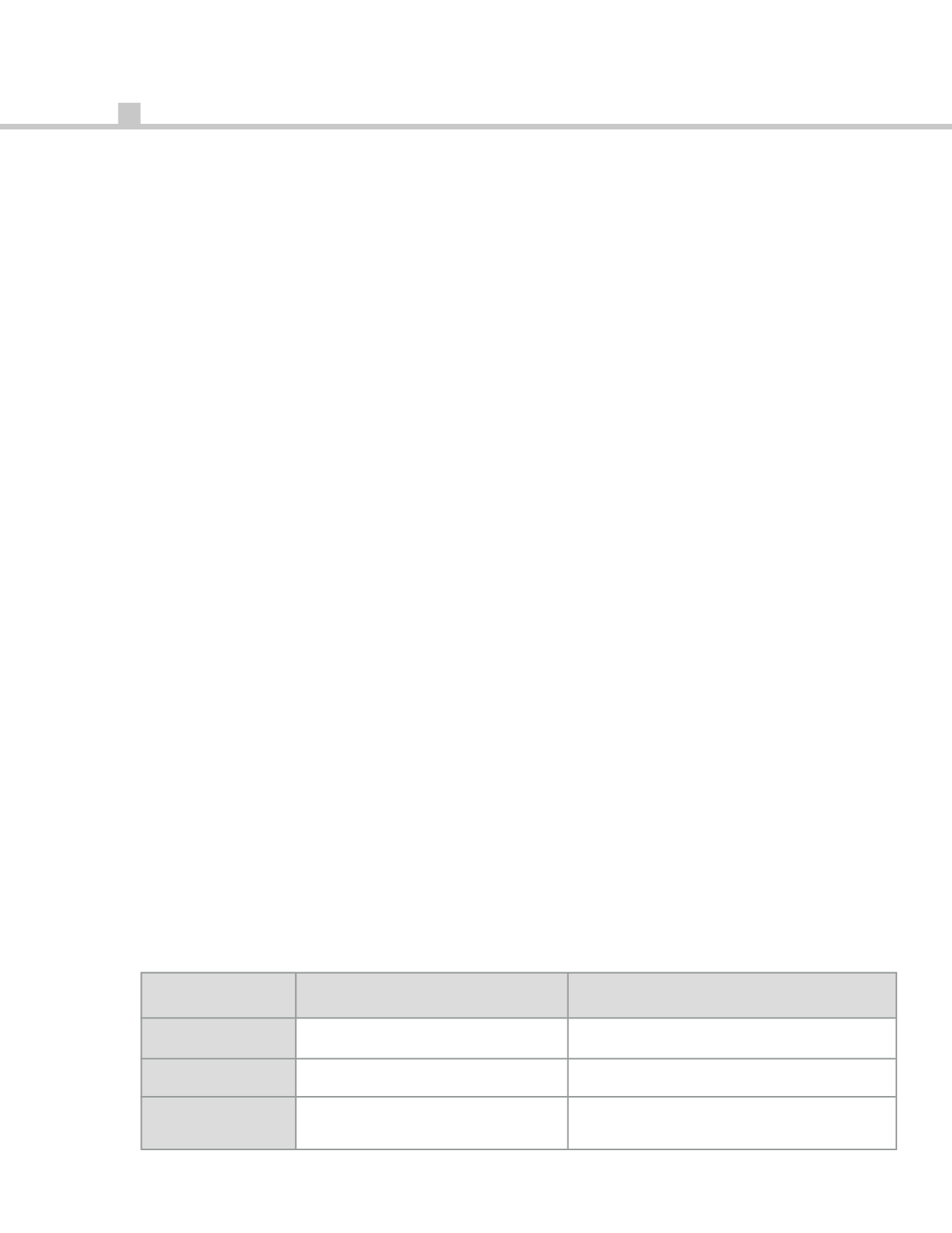
Table 2: Comparison between Subscription and Perpetual License Model.
suBscriPtion License MoDeL
PerPetuaL License MoDeL
cost
annual recurring payments.
one-time payment.
Validity
12 months.
perpetual.
entitlement
software license, support,
software license only. usually include
updates and upgrades.
1st year maintenance and support.