64
within the data center, two types of
temperature differentials are
frequently considered as a single
metric:
• the increase in air temperature as
it passes through it equipment,
picking up and removing the heat
produced within that equipment.
• the temperature differential
across the cooling equipment
cooling coils, or the difference
between supply and return air
temperatures.
frequently, these two Δt’s are
discussed as the Δt, but there are
good reasons to consider them
separately and monitor how they
differ. however, there are two
additional Δt’s beyond these that
are not commonly thought of: the
temperature differential from it
equipment exhaust to cooling unit
return and from cooling unit supply
to it equipment intake. they will
often account for unexpected
differences between the it
equipment Δt and cooling
equipment Δt.
in an ideal data center, the Δt
across the it equipment would be
the same as the Δt across the
cooling coils (or cooling source)
and there would be zero Δt
between the it exhaust and the
cooling return intake and/or
between the cooling supply and it
equipment intake. understanding
the sources of these differences can
help mitigate cooling and
inefficiency problems and help
return a data center to optimum
efficiency.
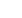
Commonly Known
ΔT: Through iT
equipment
(#1 in Figure 1)
keeping abreast of Δt’s is one of
the most important jobs in a
mission critical environment.
usually, Δt is discussed within data
centers as a single metric which is
based on the temperature drop
across cooling equipment or rise in
temperature across it equipment.
while there can be many reasons as
to why these two values may be
different, they generally fall into
two categories: either the return air
to the cooling units is being cooled
by bypass airflow or the supply air
is being warmed due to hot air re-
by
lars strong
ian seaton
how measuRing less-Commonly Known DelTa T’s
Can helP imPRove youR Cooling effiCienCy.
Figure 1: Map of the four ΔT’s